forked from datacommonsorg/website
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Repoint Terraform readme to Docsite (datacommonsorg#4872)
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
1 addition
and
245 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,247 +1,3 @@ | ||
| # Custom Data Commons Terraform Deployment | ||
|
|
||
| ## Overview | ||
|
|
||
| Deploying your own Custom Data Commons instance on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) lets you host and manage your own data while leveraging [Google's Data Commons](https://datacommons.org/) repository of publicly available information. This deployment is managed using Terraform, which automates the provisioning of infrastructure and services on GCP. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Features | ||
|
|
||
| * Creates Data Commons services container as a Cloud Run service, in region `us-central1` | ||
| * Creates Data Commons data management container as a Cloud Run job | ||
| * Enables all required Google Cloud APIs | ||
| * Creates Redis instance (optional) | ||
| * Creates Cloud SQL MySQL instance | ||
| * Creates new service account with minimum required permissions | ||
| * Automatically provisions required Google Maps API key. Stores key in GCP secrets container. | ||
| * Generates random MySQL password and stores in GCP secrets container. | ||
| * Supports multiple Data Commons instances in the same GCP account | ||
|
|
||
| ## Architecture | ||
|
|
||
| 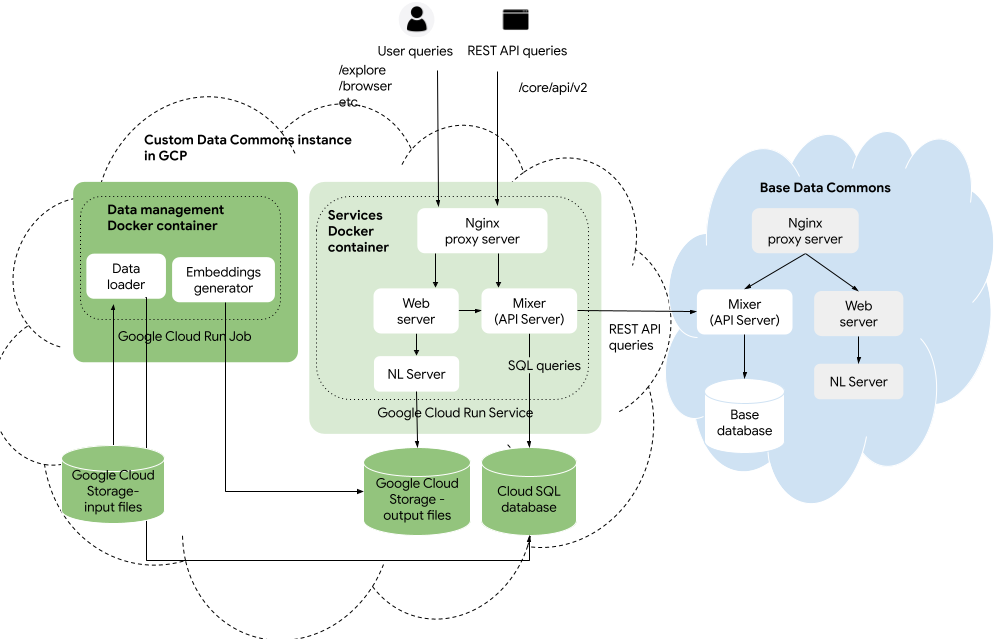 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Pre-requisites | ||
|
|
||
| - **A [Google Cloud Project](https://cloud.google.com)**: You must have a GCP project where the custom Data Commons instance will be deployed. | ||
| - **[gcloud](https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install)**: Ensure gcloud is installed on your local machine for the initial environment setup. | ||
| - **[Terraform](https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install)**: Ensure Terraform is installed on your local machine to manage the infrastructure as code. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Deployment Instructions | ||
|
|
||
| ### 1. Configure Deployment Variables | ||
|
|
||
| From the root directory of the `website` repo, create a local copy of `terraform.tfvars` file and fill in the required values. | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| cd deploy/terraform-custom-datacommons/ | ||
| cp ./modules/terraform.tfvars.sample ./modules/terraform.tfvars | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Example `terraform.tfvars`: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| project_id = "your-gcp-project" | ||
| namespace = "dan-dev" | ||
| dc_api_key = "your-api-key" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| #### Required Variables | ||
|
|
||
| - **project_id**: The Google Cloud project ID where the resources will be created. | ||
| - **namespace**: A unique namespace to differentiate multiple instances of custom Data Commons within the same project. | ||
| - **dc_api_key**: Data Commons API key. [Request an API key](https://apikeys.datacommons.org) | ||
|
|
||
| #### Optional Configuration Variables | ||
|
|
||
| - **region**: The [GCP region](https://cloud.google.com/about/locations) where resources will be deployed. | ||
| - **enable_redis**: Set to true to enable redis caching (default: false) | ||
| - **dc_web_service_image**: Docker image to use for the services container. Default: `gcr.io/datcom-ci/datacommons-services:stable`. Set to `gcr.io/datcom-ci/datacommons-services:latest` to use the latest web service image. | ||
| - **dc_data_job_image**: Docker image to use for the data loading job. Default: `gcr.io/datcom-ci/datacommons-data:stable`. Set to `gcr.io/datcom-ci/datacommons-data:latest` to use the latest data job image. | ||
| - **make_dc_web_service_public**: By default, the Data Commons web service is publicly accessible. Set this to `false` if your GCP account has restrictions on public access. [Reference](https://cloud.google.com/run/docs/authenticating/public). | ||
| - **google_analytics_tag_id**: Set to your [Google Analytics Tag ID](https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9539598) to enable Google Analytics tracking. | ||
|
|
||
| See `modules/variables.tf` for a complete list of optional variables. | ||
|
|
||
| ### 2. Set up GCP Project | ||
|
|
||
| Enables necessary APIs in your Google Cloud project: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| PROJECT_ID=your-gcp-project | ||
| ./setup.sh $PROJECT_ID | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 3. Authenticate to GCP | ||
|
|
||
| Generate credentials for Google Cloud: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| gcloud auth application-default login --project $PROJECT_ID | ||
| gcloud auth login | ||
| ``` | ||
| ### 4. (Optional) Provision a docker artifact registry and push custom Data Commons images | ||
|
|
||
| An artifact registry can optionally be used to store custom Docker images for the Data Commons web service image. | ||
|
|
||
| Create a new artifact repository named `$PROJECT_ID-artifacts` in the `us-central1` region: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| REGION=us-central1 # Or any other GCP region | ||
| ./create_artifact_repository.sh $PROJECT_ID $REGION | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Follow [these instructions to build custom Data Commons docker images](https://docs.datacommons.org/custom_dc/build_image.html). | ||
|
|
||
| For example, to build a custom Data Commons web service image: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| docker build --platform linux/amd64 -f build/cdc_services/Dockerfile \ | ||
| --tag custom-dc-services \ | ||
| . | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| And follow [these instructions to push a new image to the artifact registry](https://cloud.google.com/artifact-registry/docs/docker/pushing-and-pulling#pushing_images_to_a_repository). | ||
|
|
||
| For example: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| PROJECT_ID=your-gcp-project | ||
| docker tag custom-dc-services:latest \ | ||
| us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/$PROJECT_ID-artifacts/custom-dc-services:latest | ||
| docker push \ | ||
| us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/$PROJECT_ID-artifacts/custom-dc-services:latest | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| To use this custom image in your Terraform deployment, set the `dc_web_service_image` variable to `us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/your-gcp-project/your-gcp-project-artifacts/custom-dc-services:latest`. | ||
|
|
||
| Example: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| dc_web_service_image = "us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/my-gcp-project/datcom-website-dev-artifacts/custom-dc-services:latest" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 5. Initialize Terraform | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| cd modules | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Optionally use a Google Cloud Storage [backend](https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/settings/backends/configuration): | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| PROJECT_ID=your-gcp-project | ||
| gcloud auth application-default login --project $PROJECT_ID | ||
| gsutil mb -p $PROJECT_ID "gs://${PROJECT_ID}-datacommons-tf" | ||
|
|
||
| cat <<EOF >backend.tf | ||
| terraform { | ||
| backend "gcs" { | ||
| bucket = "${PROJECT_ID}-datacommons-tf" | ||
| prefix = "terraform/state" | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| EOF | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Initialize Terraform and validate configuration: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform init | ||
| terraform plan | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 6. Provision and run Data Commons in GCP | ||
|
|
||
| Deploy custom Data Commons instance (takes about 15 minutes): | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform apply | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Terraform will prompt you to confirm the actions before creating resources. Review the plan and type `yes` to proceed. | ||
|
|
||
| Once the deployment is complete, terraform should output something like: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| cloud_run_service_name = "<namespace>-datacommons-web-service" | ||
| cloud_run_service_url = "https://<namespace>-datacommons-web-service-abc123-uc.a.run.app" | ||
| dc_api_key = <sensitive> | ||
| gcs_data_bucket_name = "<namespace>-datacommons-data-<project-id>" | ||
| maps_api_key = <sensitive> | ||
| mysql_instance_connection_name = "<project-id>:us-central1:<namespace>-datacommons-mysql-instance" | ||
| mysql_instance_public_ip = "<mysql_ip>" | ||
| mysql_user_password = <sensitive> | ||
| redis_instance_host = "<redis_ip>" | ||
| redis_instance_port = 6379 | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 6. Load custom data | ||
|
|
||
| Upload custom sample data to the GCS bucket specified by the terraform output `gcs_data_bucket_name` (`gs://<your-namespace>-datacommons-data-<your-project-id>`). | ||
| From the `website` repository's root directory, run: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
| # Replace `NAMESPACE` and `PROJECT_ID` with values from your `terraform.tfvars` | ||
| NAMESPACE=your-namespace | ||
| PROJECT_ID=your-project-id | ||
| DATA_BUCKET=${NAMESPACE}-datacommons-data-${PROJECT_ID} | ||
| gcloud storage cp custom_dc/sample/* gs://$DATA_BUCKET/input/ | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Load custom data into data commons: | ||
| ``` | ||
| # Replace `NAMESPACE` and `REGION` with values from your `terraform.tfvars` | ||
| NAMESPACE=your-namespace | ||
| REGION=us-central1 | ||
| gcloud run jobs execute ${NAMESPACE}-datacommons-data-job --region=$REGION | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Restart the services to pick up the new data: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform apply | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 7. Open Data Commons | ||
|
|
||
| Open your Custom Data Commons instance in the browser using the above | ||
| `cloud_run_service_url` (e.g, `https://<your-namespace>-datacommons-web-service-abc123-uc.a.run.app`), | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Using Terraform Workspaces and Namespace | ||
|
|
||
| If you need to deploy multiple instances of Data Commons within the same GCP project, or across different projects, you can use Terraform workspaces and the `namespace` variable. | ||
|
|
||
| - **Workspaces**: Terraform workspaces allow you to manage multiple instances of your Terraform configuration in the same directory. To create a new workspace: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform workspace new <workspace_name> | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Switch between workspaces using: | ||
|
|
||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform workspace select <workspace_name> | ||
| ``` | ||
| - **Namespace**: The `namespace` variable helps you to prefix resource names, ensuring they don't conflict when deploying multiple instances in the same GCP project. Set the `namespace` variable uniquely for each deployment. | ||
| ### Example for Multiple Instances | ||
| To deploy multiple instances in the same project or across different projects: | ||
| 1. **Different Projects**: Specify a different `project_id` for each deployment. | ||
| 2. **Same Project**: Use different `namespace` values and Terraform workspaces to isolate the deployments. | ||
| ```bash | ||
| terraform apply -var="namespace=instance1" | ||
| ``` | ||
| Repeat the above command with a different namespace to deploy another instance. | ||
| ## Conclusion | ||
| By following these steps, you can deploy and manage custom instances of Data Commons on GCP using Terraform. This setup allows you to host your own data, integrate it with Google's public datasets, and run multiple instances within the same project or across different projects. | ||
| For more details on optional configurations, refer to the `variables.tf` file in the deployment directory. | ||
| The contents of this file have moved to https://docs.datacommons.org/custom_dc/deploy_cloud.html |