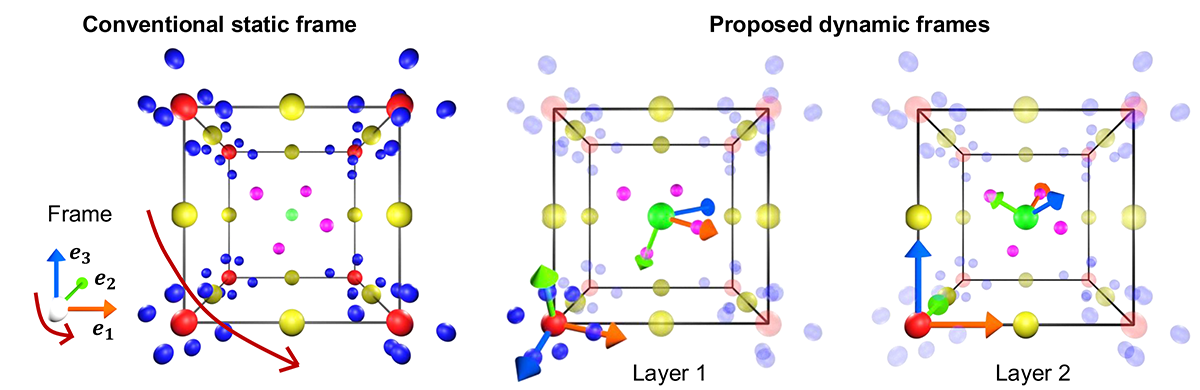
Rethinking the role of frames for SE(3)-invariant crystal structure modeling
Yusei Ito*, Tatsunori Taniai*, Ryo Igarashi, Yoshitaka Ushiku, and Kanta Ono
In The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)
@inproceedings{ito2025crystalframer,
title = {Rethinking the role of frames for SE(3)-invariant crystal structure modeling},
author = {Yusei Ito and
Tatsunori Taniai and
Ryo Igarashi and
Yoshitaka Ushiku and
Kanta Ono},
booktitle = {The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)},
year = {2025},
url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=gzxDjnvBDa}
}
Since our methodology and codebase build upon our previous work, Crystalformer, please consider citing the following paper along with the CrystalFramer paper.
@inproceedings{taniai2024crystalformer,
title = {Crystalformer: Infinitely Connected Attention for Periodic Structure Encoding},
author = {Tatsunori Taniai and
Ryo Igarashi and
Yuta Suzuki and
Naoya Chiba and
Kotaro Saito and
Yoshitaka Ushiku and
Kanta Ono
},
booktitle = {The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2024)},
year = {2024},
url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=fxQiecl9HB}
}
cd docker/pytorch21_cuda121
docker build -t main/crystalframer:latest .
docker run --gpus=all --name crystalframer --shm-size=2g -v ../../:/workspace -it main/crystalframer:latest /bin/bashNote: If docker run fails due to a relative path issue, please replace ../../ with the absolute path to the cloned repository directory.
In the docker container:
cd /workspace/data
python download_megnet_elastic.py
python download_jarvis.py # This step may take 1 hour and can be skipped for simple testing.
python download_oqmd.py In the /workspace directory in the docker container:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python train.py -p crystalframer/default_jarvis.json \
--frame_method max \
--value_pe_dist_coef 1.0 \
--value_pe_angle_wscale 4.0 \
--value_pe_angle_real 64 \
--value_pe_angle_coef 1.0 \
--save_path result \
--domain real \
--num_layers 4 \
--batch_size 256 \
--experiment_name demo \
--target_set jarvis__dft_3d_2021 \
--targets formation_energy \
Setting --value_pe_angle_real 0 yields the "Crystalformer".
In the /workspace directory in the docker container:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python train.py -p crystalframer/default_jarvis.json \
--frame_method max \
--value_pe_dist_coef 1.0 \
--value_pe_angle_wscale 4.0 \
--value_pe_angle_real 64 \
--value_pe_angle_coef 1.0 \
--save_path result \
--domain real \
--num_layers 4 \
--batch_size 256 \
--experiment_name demo \
--target_set jarvis__dft_3d_2021 \
--targets formation_energy \
Currently, the throughput gain by multi-gpu training is limited. Suggest 2 or 4 GPUs at most.
| target_set | targets | Unit | train | val | test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| jarvis__megnet | e_form | eV/atom | 60000 | 5000 | 4239 |
| jarvis__megnet | bandgap | eV | 60000 | 5000 | 4239 |
| jarvis__megnet-bulk | bulk | log(GPA) | 4664 | 393 | 393 |
| jarvis__megnet-shear | shear | log(GPA) | 4664 | 392 | 393 |
| jarvis__dft_3d_2021 | formation_energy | eV/atom | 44578 | 5572 | 5572 |
| jarvis__dft_3d_2021 | total_energy | eV/atom | 44578 | 5572 | 5572 |
| jarvis__dft_3d_2021 | opt_bandgap | eV | 44578 | 5572 | 5572 |
| jarvis__dft_3d_2021-mbj_bandgap | mbj_bandgap | eV | 14537 | 1817 | 1817 |
| jarvis__dft_3d_2021-ehull | ehull | eV | 44296 | 5537 | 5537 |
| jarvis__oqmd_3d | stability | eV/atom | 654108 | 81763 | 81763 |
| jarvis__oqmd_3d | delta_e | eV/atom | 654108 | 81763 | 81763 |
| jarvis__oqmd_3d-bandgap | bandgap | eV | 653388 | 81673 | 81673 |
To use a default hyperparameter set, please use default_mp.json for --target_set jarvis__megnet, default_jarvis.json for --target_set jarvis__dft_3d_2021, and default_oqmd.json for --target_set jarvis__oqmd.
General training hyperparameters:
n_epochs(int): The number of training epochs.batch_size(int): The batch size (i.e., the number of materials per training step).loss_func(L1|MSE|Smooth_L1): The regression loss function form.optimizer(adamw|adam|): The choice of optimizer.adam_betas(floats): beta1 and beta2 of Adam and AdamW.lr(float): The initial learning rate. The default setting (5e-4) works mostly the best.lr_sch(inverse_sqrt_nowarmup|const): The learning rate schedule.inverse_sqrt_nowarmupsets learning rate tolr*sqrt(t/(t+T))where T is specified bysch_params.constuses a constant learning ratelr.
Final MLP's hyperparameters:
embedding_dim(ints): The intermediate dims of the final MLP after pooling, defining Pooling-Repeat[Linear-ReLU]-FinalLinear. The default setting (128) defines Pooling-Linear(128)-ReLU-FinalLinear(1).norm_type(no|bn): Whether or not use BatchNorm in MLP.
Transformer's hyperparameters:
num_layers(int): The number of self-attention blocks. Should be 4 or higher.model_dim(int): The feature dimension of Transformer.ff_dim(int): The intermediate feature dimension of the feed-forward networks in Transformer.head_num(int): The number of heads of multi-head attention (HMA).domain(real|multihead|real-reci): Whether use reciprocal-space attention by parallel MHA (multihead) or block-wisely interleaving between real and reciprocal space (real-reci). When reciprocal-space attention is used,scale_reciandgauss_lb_recican also be specified. Crystalframer supports only therealmode.
Distance-based edge feature's hyperparameters:
-
scale_real(float or floats): "r_0" in the paper. (Passing multiple values allows different settings for individual attention blocks.) -
gauss_lb_real(float): The bound "b" for the rho function in the paper. -
value_pe_dist_real(int): The number of Gaussian basis functions for distance (i.e., "D" for$\boldsymbol{b_\text{dist}}$ in the paper). Should be a multiple of 16. -
value_pe_dist_wscale(float): Scaling factor for width of Gaussian basis function for distance (i.e., "s" for$\boldsymbol{b_\text{dist}}$ in the paper). -
value_pe_dist_coef(float): Scaling factor for Gaussian basis function for length (i.e., "c_{dist}" in the paper). -
value_pe_dist_max(float): "r_max" in the paper. A positive value directly specifies r_max in Å, while a negative value specifies r_max via r_max = (-value_pe_dist_max)*scale_real.
Frame-based edge feature's hyperparameters:
-
frame_method(max|weighted_pca|max_static|pca|lattice): Frame construction methods. -
value_pe_angle_real(int): The number of Gaussian basis functions for angle (i.e., "D" for$\boldsymbol{b_\text{angl}}$ in the paper). Should be a multiple of 16. Setting 0 yields the "Crystalformer". -
value_pe_angle_wscale(float): Scaling factor for width of Gaussian basis function for angle (i.e., "s" for$\boldsymbol{b_\text{angl}}$ in the paper). -
value_pe_angle_coef(float): Scaling factor for Gaussian basis function for angle (i.e., "c_{angl}" in the paper).
- The model currently supports crystal structures with up to 320 atoms per unit cell.
For each of train, val, and test splits, make a list of dicts containing pymatgen's Structures and label values:
- list
- dict
- 'structure': pymatgen.core.structure.Structure
- 'property1': a float value of
propety1of this structure - 'property2': a float value of
propety2of this structure - ...
- dict
Dump the list of each split in a directory with your dataset name as
import os
import pickle
target_set = 'your_dataset_name'
split = 'train' # or 'val' or 'test'
os.makedirs(f'data/{target_set}/{split}/raw', exist_ok=True)
with open(f'data/{target_set}/{split}/raw/raw_data.pkl', mode="wb") as fp:
pickle.dump(data_list, fp)Then, you can specify your dataset and its target property name as
python train -p latticeformer/default.json \
--target_set your_dataset_name \
--targets [property1|property2] \Copyright © 2025 OMRON SINIC X Corporation. All Rights Reserved.